Abstract [View PDF] [Read Full Text]
Objective
To investigate the inhibitory effect of RMT1-10-induced tolerogenic dendritic cells (Tol-DCs) in vitro on high-risk corneal allograft rejection in mice and its mechanism.
Methods
One hundred SPF male BALB/c mice and fifty SPF male C57BL/6 mice were selected.Bone marrow-derived immature dendritic cells (imDCs) obtained from C57BL/6 mice were divided into imDCs group, mature dentritic cells (mDCs) group, RMT1-10 group, and IgG isotype control group.The imDCs in the four groups were cultured with no intervention, lipopolysaccharide, RMT1-10 and lipopolysaccharide, or IgG isotype antibody and lipopolysaccharide for 7 days according to grouping.The expression levels of different phenotypes of DCs including CD11c, CD80, CD86, major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-Ⅱ, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain containing molecule (Tim)-4 and CD103 in the four groups were detected by flow cytometry.The concentrations of interleukin-10 (IL-10) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in the DCs supernatants were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.A mixed lymphocyte culture system was established, and the stimulation index (SI) of CD4+ T cell proliferation stimulated with DCs was detected by cell counting kit 8 method.Corneal neovascularization was induced by corneal stromal suture in BALB/c mice, and the 80 mice with neovascularization in 4 quadrants growing into the middle and peripheral cornea were used as recipients.The recipient mice were randomized into imDCs group, mDCs group, RMT1-10 group, and IgG isotype control group using the random number table method, with 20 mice in each group.An injection of corresponding DCs (1×106 cells/100 μl) was administered to the recipient mice via the tail vein according to grouping.At 7 days following the injection, C57BL/6 mice were used as donors and penetrating keratoplasty was performed.Within one month after the operation, signs of corneal grafts rejection, including opacity, edema and neovascularization, were observed by slit lamp biomicroscopy and scored every day.At 21 days after the operation, 5 recipients selected from each group were subcutaneously injected with naive C57BL/6 splenocytes (1×106 cells/100 μl) behind the ear.The delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) was evaluated by ear swelling at 24 hours after the subcutaneous injection.The use and care of experimental animals complied with the Regulations on the Management of Experimental Animals promulgated by the State Science and Technology Commission.This study protocol was approved by an Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University (No.CYFYLL2020055).
Results
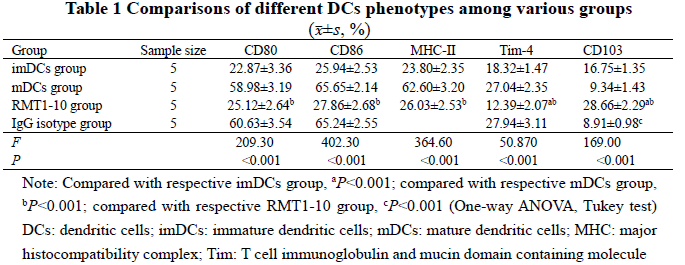
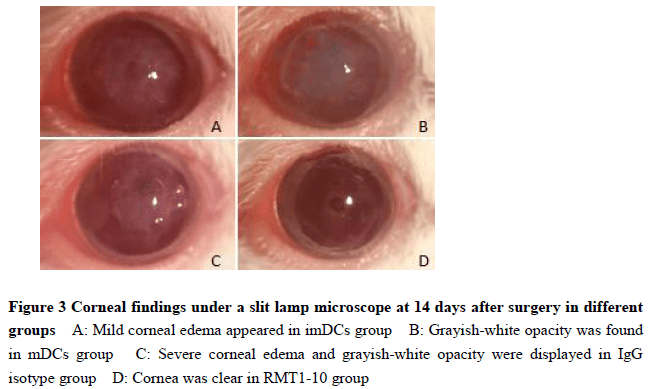
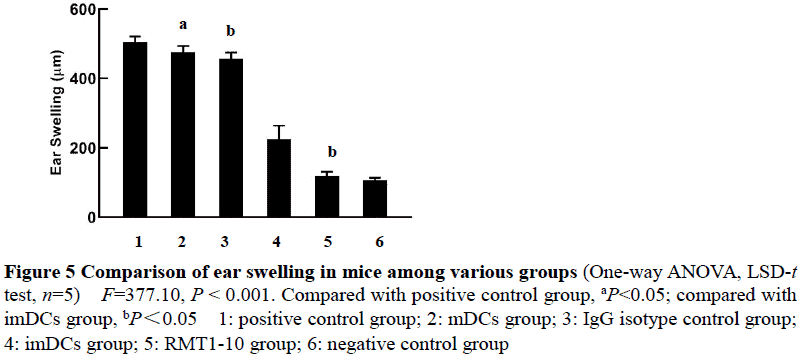
Compared with mDCs group, the expressions of CD80, CD86 and MHC-Ⅱ, and the percentage of Tim-4-positive cells in CD11c-positive cells were significantly decreased in RMT1-10 group, showing statistically significant differences (all at P<0.001). The percentage of Tim-4-positive cells were significantly decreased in RMT1-10 group than imDCs group, and the percentage of CD103-positive cells in RMT1-10 group was significantly higher than imDCs group, mDCs group and IgG isotype control group (all at P<0.001). The concentrations of IL-10 and TGF-β in the cell culture supernatant of RMT1-10 group were significantly higher than those of the other three groups, with statistically significant differences (all at P<0.001). There were statistically significant differences in the SI of CD4+ T cell proliferation simulated by DCs (Fgroup=1 833.00, P<0.001; Fratio=230.40, P<0.001; Finteraction=3.06, P=0.01). The SI of DCs/CD4+ T cells ratio at 1∶5, 1∶10, 1∶20 and 1∶40 were all significantly lower in imDCs group than mDCs group, and were all significantly lower in RMT1-10 group than imDCs group (all at P<0.05). There was a statistically significant difference in corneal graft survival curve among various groups (χ2=77.69, P<0.001). The survival rate of RMT1-10 group was significantly higher than that of imDCs group (χ2=9.74, P=0.002), and the survival rate of imDCs group was significantly higher than that of mDCs group (χ2=31.02, P<0.001). The ear swelling of recipient mice of positive control group, mDCs group, IgG isotype control group, imDCs group and RMT1-10 group was (503.6±17.2), (475.7±17.6), (456.2±18.8), (225.2±39.4), (118.1±12.6), and (106.4±7.4) μm, with a statistically significant difference among them (F=377.10, P<0.001). The mice ear swelling was more serious in positive control group than mDCs group, more serious in IgG isotype control group than imDCs group, and more serious in imDCs group than RMT1-10 group (all at P<0.05).
Conclusions
RMT1-10 can inhibit the rejection of high-risk corneal transplantation in mice, the mechanism of which may be attributed to inducing imDCs to transform into Tol-DCs in vitro and up-regulating the expression of TGF-β and IL-10, which promotes antigen-specific immune tolerance after adoptive transfer, thereby indirectly prolongs the survival of corneal grafts.
Key words:
Figures and tables



Contributor Information
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Chengde Central Hospital, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China