Abstract [View PDF] [Read Full Text]
Objective
To investigate the imaging features of iris fluorescein angiography (IFA) combined with fluorescein fundus angiography (FFA) in diabetic iridopathy.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted.Sixty-five eyes of 44 patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) combined with diabetic iridopathy (DI) were enrolled in Henan Eye Hospital from May 2013 to May 2020.Patients were divided into non-proliferative diabetic iridopathy (NPDI) group and rubeosis iridis group according to the imaging results.Ophthalmic examinations including visual acuity, intraocular pressure, slit lamp miacroscopy, IFA and FFA were carried out in all patients.IFA was used to detect the iris imaging characteristics and the regression time of fluorescein in anterior chamber, and FFA was used to observe the retinal image characteristics and the incidence of optic disc neovascularization.To avoid the statistical error of recording the IFA examination time of the contralateral eye, only the relevant data of the affected eyes were analyzed.This study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki.The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Henan Eye Hospital (No.HNEECKY-2020[06]). Written informed consent was obatined from all patients before any medical examination.
Results
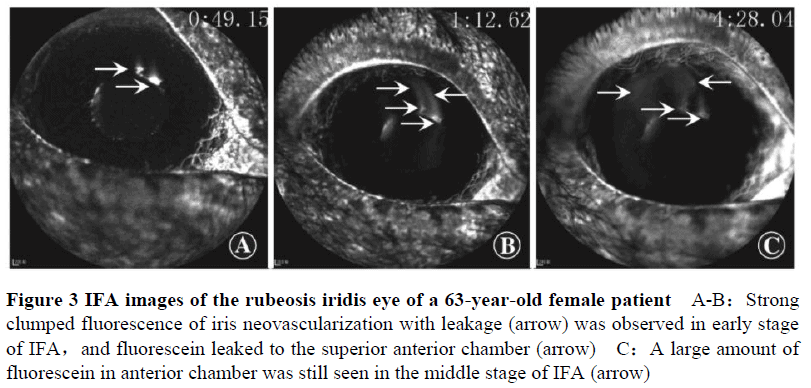
Among the patients, 30 cases (50 eyes) were with NPDI and 14 cases (15 eyes) were with rubeosis iridis.The fluorescein regression time in anterior chamber of NPDI group was (3.37±0.11) minutes, which was significantly shorter than (6.02±0.29) minutes of rubeosis iridis group (t=8.541, P<0.001). Strong fluorescence of retinal neovascularization was observed in both groups.The incidence of optic disc neovascularization in NPDI group was 20% (6/30), which was significantly lower than 50% (7/14) in rubeosis iridis group (P=0.04).
Conclusions
Diabetic rubeosis iridis can be diagnosed by the imaging features of IFA and the fluorescein regression time in anterior chamber.PDR combined with optic disc neovascularization should be evaluated by FFA combined with IFA.
Key words:
Contributor Information
Department of Ophthalmology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Henan Eye Hospital, Henan Eye Institute, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Henan Eye Hospital, Henan Eye Institute, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Henan Eye Hospital, Henan Eye Institute, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Henan Provincial People’s Hospital, Henan Eye Hospital, Henan Eye Institute, Zhengzhou University People’s Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, China