Abstract [View PDF] [Read Full Text]
Objective
To investigate the inhibitory effect of melatonin on pyroptosis of lens epithelium cells (HLECs) induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and its mechanism.
Methods
The cultured HLECs were divided into normal control group, model control group, melatonin group, vitamin E group, and vitamin E solvent group.Cells in melatonin group, vitamin E group and vitamin E solvent group were pre-cultured with 1×10-6 mol/L melatonin, 100 μmol/L vitamin E or equal volume of vitamin E solvent, then cultured with 100 μmol/L H2O2, respectively, and the cells in the normal control group and model control group were cultured with normal condition or 100 μmol/L H2O2, respectively.The HLECs transfected with nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 short hairpin RNA (shNrf2) or shNrf2 negtive control lentivirus and following with 100 μmol/L H2O2 treatment were served as shNrf2 group and shNrf2 negative control group, respectively; and the transfected cells treated with 1×10-6 mol/L melatonin and subsequent 100 μmol/L H2O2 treatment were served as melatonin+ shNrf2 group and melatonin+ shNrf2 negative control group.The activity of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) and the expression levels of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 in the culture supernatant were detected by the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit.The concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was assessed by flow cytometry.The expression level of Nrf2, NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain (ASC), caspase-1 p20 and GSDMD-N proteins were evaluated by Western blot.
Results
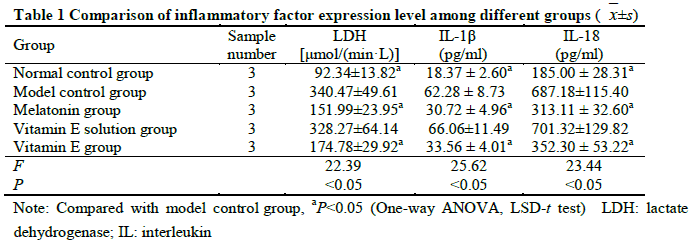
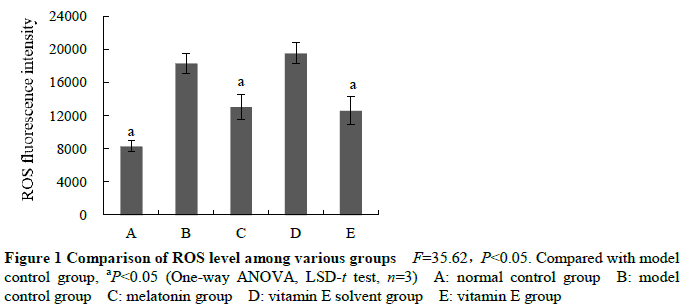
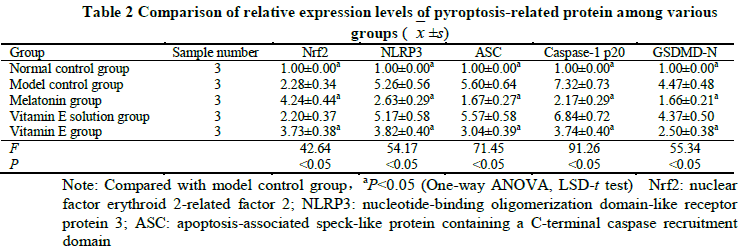
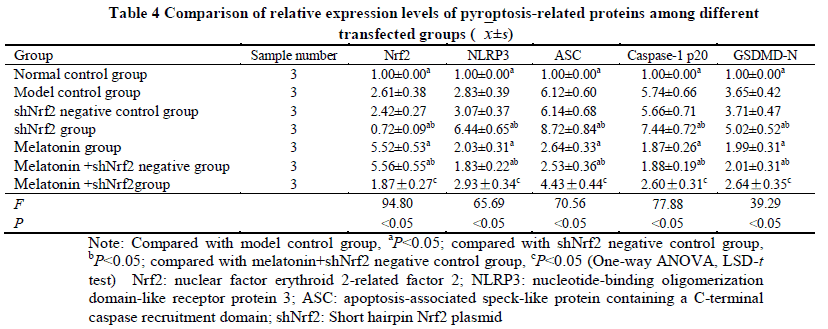
Compared with model control group, the activity of LDH and the concentrations of IL-1β and IL-18 were significantly decreased in melatonin group and vitamin E group, showing statistically significant differences (all at P<0.05). The ROS fluorescence intensities were 13 040.67±1 550.66 and 12 593.67±1 677.06 in melatonin group and vitamin E group, respectively, which were significantly lower than 18 310.33±1 248.01 in model control group (both at P<0.05). The relative expression levels of Nrf2 protein were 4.24±0.44 and 3.73±0.38 in melatonin group and vitamin E group, respectively, which were significantly higher than 2.28±0.34 in model control group, and the relative expression levels of NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 p20 and GSDMD-N in melatonin group and vitamin E group were significantly decreased than model control group (all at P<0.05). The relative expression level of Nrf2 protein in shNrf2 group and melatonin+ shNrf2 group was significantly reduced, and the expression levels of LDH, IL-1β, IL-18, ROS content, NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 p20 and GSDMD-N were significantly increased in comparison with shNrf2 negative control group and melatonin+ shNrf2 negative control group, respectively (all at P<0.05).
Conclusions
Melatonin can inhibit the release of NLRP3 inflammasome by activating Nrf2, and has an inhibitory effect on the pyroptosis of HLECs.
Key words:
Figures and tables





Contributor Information
Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China