Abstract [Download PDF] [Read Full Text]
Objective
To study the effect and mechanism of angiotensin type 1 receptor (AGTR1) blocker olmesartan (OMS) on the apoptosis of human Tenon capsule fibroblasts (HTF).
Methods
Tenon capsule tissues were obtained from patients during strabismus surgery in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University.Primary HTF were cultured by explant culture.Primary cells were identified by vimentin immunofluorescence staining and flow cytometry.The fibrosis model of HTF was established using 10 ng/ml transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2). The cells were divided into normal control group cultured in culture medium, TGF-β2 group in culture medium containing TGF-β2, TGF-β2+ OMS group in culture medium containing TGF-β2 and OMS, and OMS group in culture medium containing OMS, and were cultured for 48 hours.Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry with annexin V/PI staining.The early apoptosis, late apoptosis, and total apoptosis rates were analyzed.The protein expression of procaspase-9, cleaved caspase-9, bax and bcl-2 in the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway was detected by Western blot.The activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) was detected by colorimetry.The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (No.2019-014).
Results
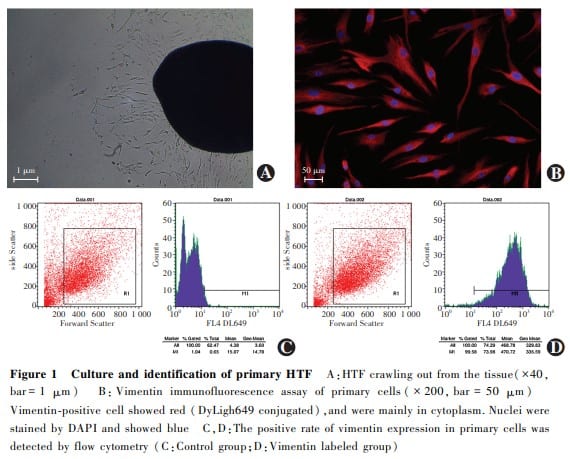
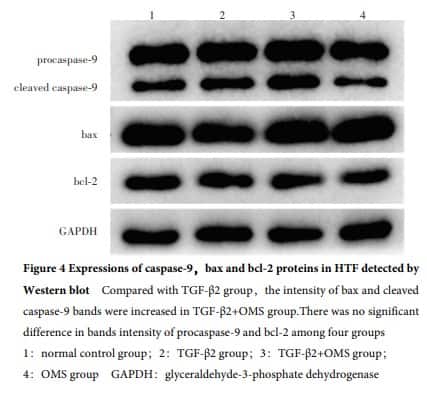
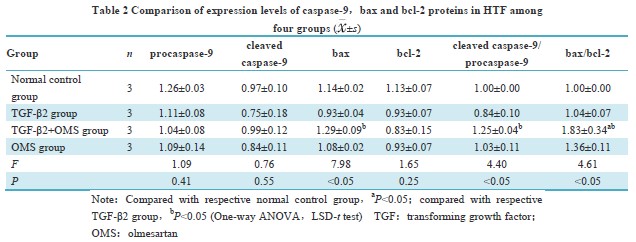
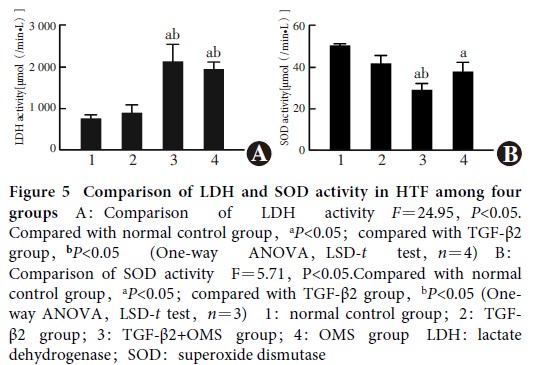
Primary HTF were successfully isolated and cultured.The cultured cells were long spindle-shaped and positive for vimentin.The expression rate of vimentin in the primary cells was greater than 99%.A statistically statistical difference was found in the early apoptosis rate, late apoptosis rate, and total apoptosis rate among the four groups (F=24.92, 3.96, 41.82; all at P<0.05). The early and total apoptosis rates were significantly higher in TGF-β2+ OMS group than normal control group and TGF-β2 group, and the late apoptosis rate in TGF-β2+ OMS group was significantly higher than that of normal control group (all at P<0.05). There were statistically significant differences in cleaved caspase-9/procaspase-9, bax, and bax/bcl-2 among the four groups (F=4.40, 7.98, 4.61; all at P<0.05). The bax/bcl-2 expression was significantly increased in TGF-β2+ OMS group in comparison with normal control group, and the expressions of cleaved caspase-9/procaspase-9, bax, and bax/bcl-2 were significantly elevated in TGF-β2+ OMS group compared with TGF-β2 group (all at P<0.05). LDH activity in the normal control group, TGF-β2 group, TGF-β2+ OMS group and OMS group was (783.99±79.97), (913.16±196.86), (2 529.06±240.21), and (2 134.29±138.96) μmol/(min·L), respectively, showing a statistically significant difference (F=24.95, P<0.05). Compared with normal control group and TGF-β2 group, LDH activity in TGF-β2+ OMS group was increased, and the differences were statistically significant (both at P<0.05). SOD activity in the normal control group, TGF-β2 group, TGF-β2+ OMS group and OMS group was (50.35±0.97), (41.61±4.56), (28.88±3.26), and (37.61±4.83) μmol/(min·L), respectively, showing a statistically significant difference (F=5.71, P<0.05). SOD activity was reduced in TGF-β2+ OMS group compared with normal control group and TGF-β2 group, reduced in OMS group compared with normal control group, and the differences were statistically significant (all at P<0.05).
Conclusions
AGTR1 blocker OMS can promote the apoptosis of HTF effectively.Mitochondrial apoptosis pathway mediated by bax/bcl-2/caspase-9 and oxidative stress pathway are the potential mechanisms that OMS regulates the apoptosis of HTF.
Key words:
Figures&Tables



Contributor Information
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China
Department of Ophthalmology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, China