Abstract [View PDF] [Read Full Text]
Objective
To study the effect of ZhuJing pill variant formula medicated serum on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of human retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells and its mechanism.
Methods
Thirty female SPF grade SD rats aged 2 months old were selected.The rats were randomized into blank control group and Zhujing pill variant formula group according to random number table method, with 15 in each group, which were intragastrically administered with normal saline and ZhuJing pill variant formula solution for 7 days accordingly to prepare blank control serum and medicated serum.ZhuJing pill variant formula medicated serum was prepared with SD rats.ARPE-19 cells were divided into normal control group, model control group, blank serum group as well as 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups, SB216763 group and SB216763+ medicated serum group.Normal and blank control groups were cultured in normal culture medium, while the other six groups were cultured in blank rat serum medium, medicated serum medium of corresponding concentration, 10 μmol/L SB216763 medium and 10 μmol/L SB216763+ 10.0% medicated serum medium, respectively.Normal control group was routinely cultured, while the other groups were routinely cultured for 24 hours, and then added with H2O2 with the final concentration of 200 μmol/L for 24 hours.Cell viability was assessed by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and cell migration ability was detected by Transwell assay.Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was detected by dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay, and MDA level was identified by sulfhydryl barbituric acid assay.The expression levels of Nrf2 pathway related proteins including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO-1) and EMT-related proteins including transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2), protein kinase B (AKT), glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), snail family zinc finger 1 (SNAIL1), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) in cells were measured by western blot assay.The use and care of animals complied with Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals.
Results
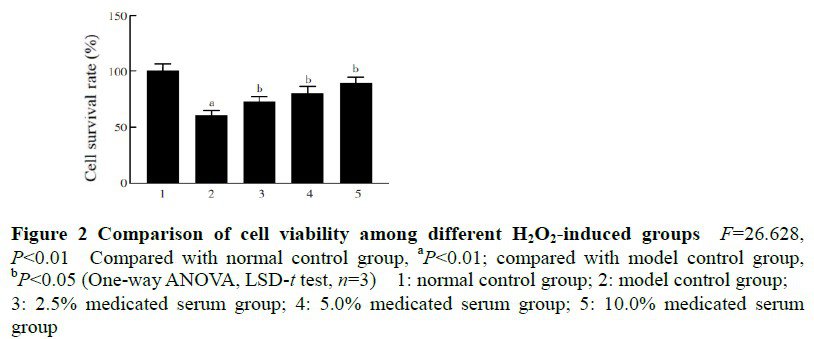
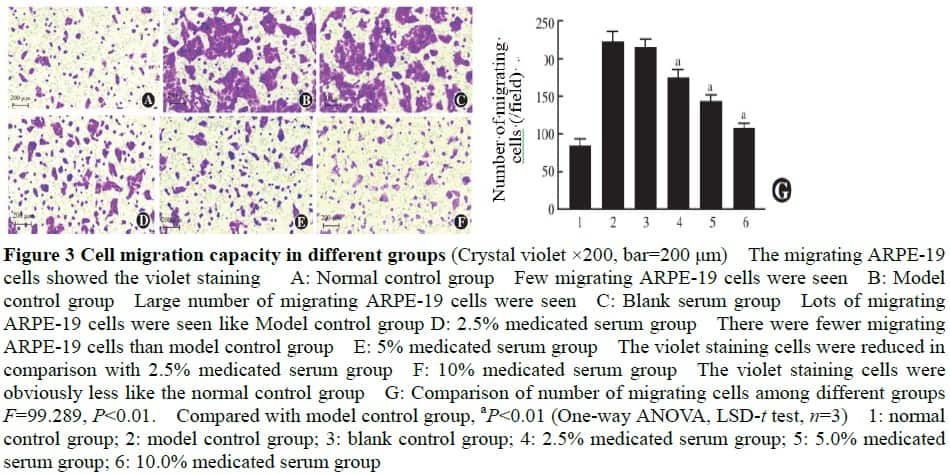
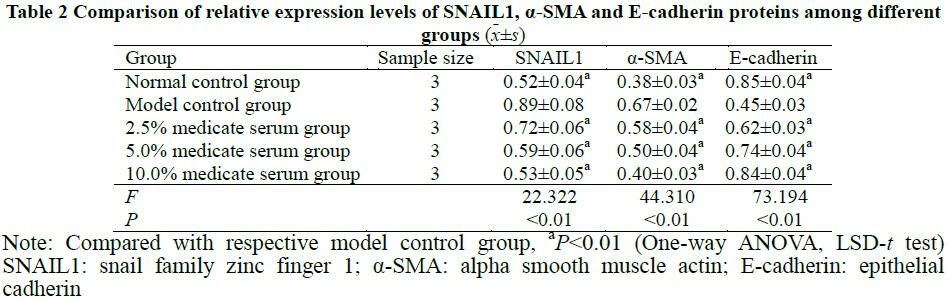
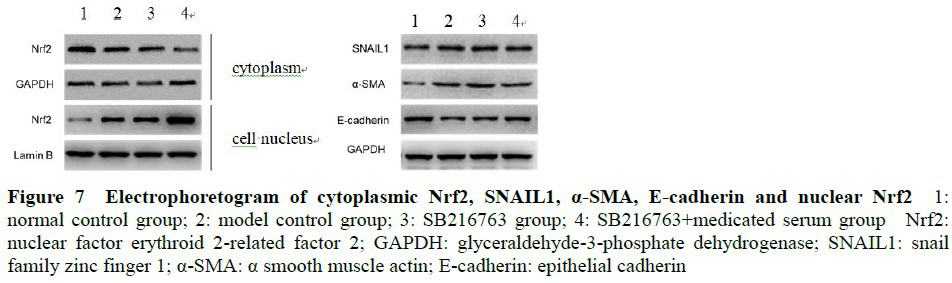
There was no significant difference in cell survival rate among blank serum group, 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups (F=0.163, P>0.05). The cell survival rates were (100.50±5.91)%, (60.87±4.30)%, (73.27±4.46)%, (80.73±5.67)% and (89.90±4.97)% in normal control group, model control group, 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups, and the number of migrating cells was (84.67±8.33), (222.33±13.58), (215.67±10.02), (174.67±10.60), (143.67±8.02) and (107.67±6.66) pcs/visual field in normal control group, model control group, blank serum group, 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups, respectively, with significant differences among the groups (F=26.628, 99.289; both at P<0.01). The contents of ROS and MDA in model control group were significantly increased in comparison with normal control group (both at P<0.01). The contents of ROS and MDA of 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups were significantly decreased in comparison with model control group (all at P<0.01). The relative expression levels of SNAIL1, α-SMA, TGF-β2, p-AKT and p-GSK-3β proteins were significantly higher and the relative expression level of E-cadherin protein was significantly lower in model control group compared with normal control group, 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups (all at P<0.05). Compared with normal control group, the relative expression level of cytoplasmic Nrf2 in model control group was decreased, while the relative expression levels of nuclear Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO-1 were increased, and the differences were statistically significant (all at P<0.05). Compared with model control group, the relative expression levels of cytoplasmic Nrf2 in 2.5%, 5.0% and 10.0% medicated serum groups were reduced, and the relative expression levels of nuclear Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO-1 were enhanced, and the differences were statistically significant (all at P<0.01). Compared with model control group, the relative expression level of cytoplasmic Nrf2 in SB216763 group was decreased, and the relative expression level of nuclear Nrf2 was increased, and the differences were statistically significant (both at P<0.05). Compared with SB216763 group, the relative expression levels of cytoplasmic Nrf2, SNAIL1 and α-SMA in SB216763+ medicated serum group were decreased, and the relative expression levels of nuclear Nrf2 and E-cadherin protein were increased, and the differences were statistically significant (both at P<0.05).
Conclusions
ZhuJing pill variant formula medicated serum can inhibit H2O2-induced EMT in ARPE-19 cells.The mechanism may be related to the inhibition of AKT/GSK-3β pathway and the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Key words:
Figures&Tables







Contributor Information
Department of Ophthalmology, Liyang Branch of Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang 213300, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Liyang Branch of Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang 213300, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Liyang Branch of Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Liyang 213300, China
Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, China